lxqt-policykit
Overview
lxqt-policykit is the polkit authentification agent of LXQt.
polkit is a software framework to handle privileges of processes.
In LXQt it is e. g. used to extend the privileges of the GUI tools of lxqt-admin. These are launched by a regular user. But in order to apply the settings they deal with root privileges are needed and acquired via polkit.
Among the various components of polkit the authentication agent is the one to query the user for credentials by dialogue windows like this one of lxqt-policykit.
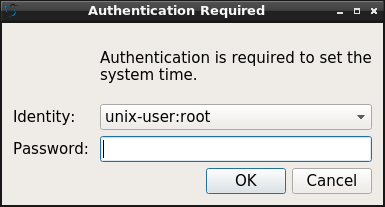
While there's only a single implementation of all other polkit components various different authentication agents are provided by the various desktop environments. Basically these can be used interchangeably, that is lxqt-policykit can be used in an LXDE session or lxpolkit, the authentication agent of LXDE, can be used in an Xfce session. Most of the time it's better to use the implementation provided by a distinct desktop environment as it integrates better, though.
Technically, lxqt-policykit is just a single binary lxqt-policykit-agent which is running as LXQt Module and launching the GUI on demand.
Note that the naming lxqt-policykit is strictly speaking an anachronism. It refers to Policykit which was the predecessor of polkit. The name wasn't changed when Policykit was replaced by polkit as both provide roughly the same features albeit they are technically different.
Installing
Compiling sources
Runtime dependencies are polkit-qt5 and liblxqt.
Additional build dependencies are CMake and optionally Git to pull latest VCS checkouts. The localization files were outsourced to repository lxqt-l10n so the corresponding dependencies are needed, too. Please refer to this repository's README.md for further information.
Code configuration is handled by CMake. CMake variable CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX has to be set to /usr on most operating systems.
To build run make, to install make install which accepts variable DESTDIR as usual.
Binary packages
Arch Linux
The latest release is provided by package lxqt-policykit in repository community, the actual master checkout can be
compiled by packages lxqt-policykit-git from the AUR.
Debian
Package lxqt-policykit is available in the official repositories as of Debian stretch. For now it is comprising the
translations as well but these will probably be outsourced in package lxqt-policykit-l10n one day.
Fedora
Package lxqt-policykit is available as of Fedora 22.
openSUSE
Package lxqt-policykit is providing the binary, lxqt-policykit-lang the translations. Both are available as of
openSUSE Leap 42.1.
Configuration, Usage
Like all LXQt Modules lxqt-policykit-agent can be adjusted from section "Basic Settings" in configuration dialogue LXQt Session Settings of lxqt-session.
From a user's point of view the usage is limited to interacting with the GUI as seen above.